A workflow for effective transfections
Alexander Kunz
04.03.2025
Ansys CFD, Ansys Rocky and the Stochos AI solution in biotechnology
Transfections, i.e. the introduction of foreign DNA or RNA into human cells to manipulate human genetic information, is a promising approach to help people with rare or incurable genetic diseases. For this to be possible, the high complexity and susceptibility of the procedure must be mastered. An innovative workflow developed by APC makes an important contribution here. It relies on simulations and artificial intelligence.

© Getty Images
The clients of APC, a highly innovative, bioscience-driven company based in Dublin, Ireland, share a common mission: to save lives. APC's team of process development experts - chemical and bioprocess engineers, organic and process chemists, bioprocess scientists, and modeling and simulation specialists - use their unique knowledge to help these biopharmaceutical companies develop new processes based on the latest science and technology.
A current project, which has attracted a great deal of attention at several specialist conferences, is concerned with gene therapies. The APC team also used simulation and AI tools.
Transfections: a key to advance gene therapies
Gene therapy seeks to modify or manipulate the expression of a gene or to alter the biological properties of living cells for therapeutic use (FDA & Cber, 2020). Transfection is the process by which nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) are introduced into eukaryotic cells utilizing means other than viral infection (Mancinelli et al., 2021).
Although transfections are promising to treat incurable, rare, and inherited genetic diseases, they are complex and most commonly display low productivity. Furthermore, they are difficult to scale, and display high levels of impurities.
Thus, the APC team opted for a model and simulation workflow for transfection development as an alternative to increase process understanding and reduce the time and cost of process development.
Project overview
Every transfection process development has always typical objectives, e.g. ensuring the quality and quantity of DNA going into the cells or maximizing recovery of transfected viable cells. The model-driven workflow gives new options to gain additional important insights, that are not possible with traditional approaches based on experiments, or only with disproportionate effort.
Examples:
- Ensure good mixing conditions for cell health by using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations
- Identify process conditions that maximize the likelihood of transfection by coupling CFD simulations with Discrete Element Methods (DEM) to model cells and complexes of plasmids and PEI as particles
- Further optimize the process by using artificial intelligence (AI) models
The model-based workflow is closely interlinked with the experimental approach at every point. This is partly because the experimental data is an important input, and partly for validation reasons. The experimental calibration and validation was supported by the Irish Research Council EBPPG/2022/38. The workflow diagram also shows where simulations and artificial intelligence were used. Their contribution is outlined below.

The complete workflow | © APC
Optical simulation
Precision & efficiency combined. Find out in our webinars and further information how you can develop your optical designs with maximum precision.
Ansys Startup Program: simulation for startups
Take advantage of the best in simulation technology, right from the start of your business, with a reduced investment.

AI for Engineers in Simulation and Product Development
Learn about the current AI technologies, emerging trends, and how to apply AI to your simulation tasks.
![ai-for-engineers-in-simulation-and-product-development-21202[1]](https://blog.cadfem.net/hubfs/02_TOPICS/DE_Corporate%20Newsletter/03-August%202024/ai-for-engineers-in-simulation-and-product-development-21202%5B1%5D.jpg)
CFD/DEM simulation results
CFD and DEM simulations were used to accelerate development by replacing some experiments. CFD and DEM simulations were performed using the Ansys Fluent® and Ansys Rocky™ software on AWS cloud computers. CADFEM UK & Ireland supported the model setup and the execution of the simulations.
CFD simulation goals overview:
- Mixing time determination
- Shear and energy dissipation quantification and control to avoid cell damage
- Oxygen distribution characterization and optimization
- Investigation and elimination of classification and poorly mixed internal zones
DEM simulation goals overview:
The hypothesis was that the process conditions that display the highest number of collisions between cells and complexes in the simulations, would display the highest transfection efficiency in the real system.

CFD: Simulation of hydrodynamic shear stress | © APC

Bayesian Optimization
Neural Networks and Gaussian Processes were tested against traditional DoE and provided faster insights to reduce the experimental burden and accelerate data analysis. The AI model used was developed in collaboration with PI Probabiligence, using their STOCHOS platform.
Two models were developed:
- Using experimental data: optimization goal was to maximize the percentage of cells that contain GFP (green fluorescent protein) and cell viability after transfection.
- Using in-silico data: optimization goal was to maximize the CFD-DEM simulated cumulative number of collisions
An additional statistical analysis was then performed to infer if the results obtained from the in-silico data resulted in the same optimization suggestion as the experimental study would.
The feedback from the pd2m conference was encouraging. Experts confirmed that the workflow was well-rounded, from planning to model selection and execution of experimental and simulation work.
Less experiments, increased process knowledge
The proposed workflow identified the optimized critical process parameters (CPPs) setpoint that maximizes the number of collision cells/complexes while ensuring cell viability. CFD/DEM was used for designing the process, increasing process understanding, and to accelerating development.
This workflow is transferable to other transfection systems and reduces typical process development costs by replacing expensive physical experiments with simulations, reducing the number of experiments required to achieve target yield and increased mechanistic understanding of the process.
About this article
This article summarizes the presentation “Model and Simulation workflow for Transfection Development” of Ana Luiza Pinto Queiroz, Digital Engineering Lead, APC, held at the The Pharmaceutical Discovery, Development and Manufacturing Forum 2024 (P2DM).
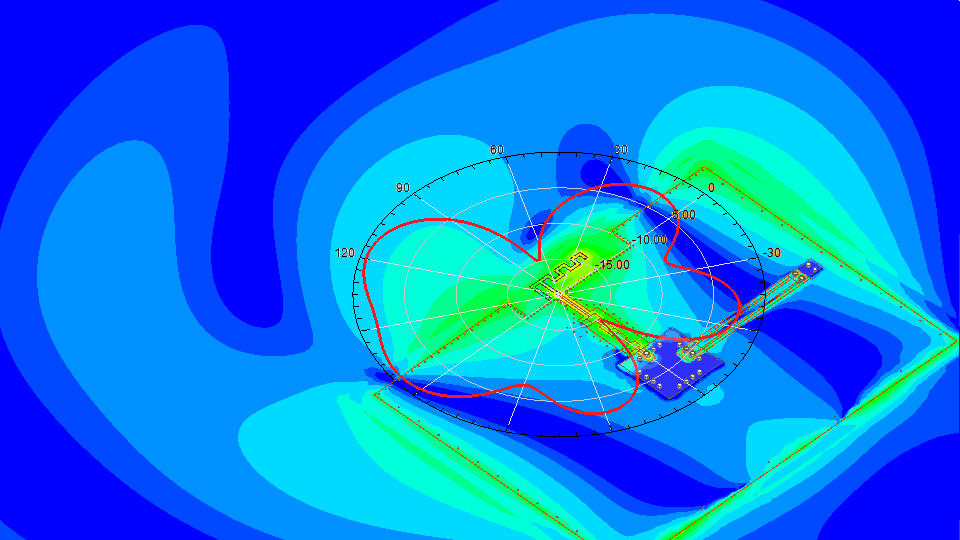
Ansys HFSS
Industry standard for determining the radiation and transmission behavior of high-frequency electromagnetic fields.